The vagus nerve quietly orchestrates and regulates essential bodily functions, often without your awareness.
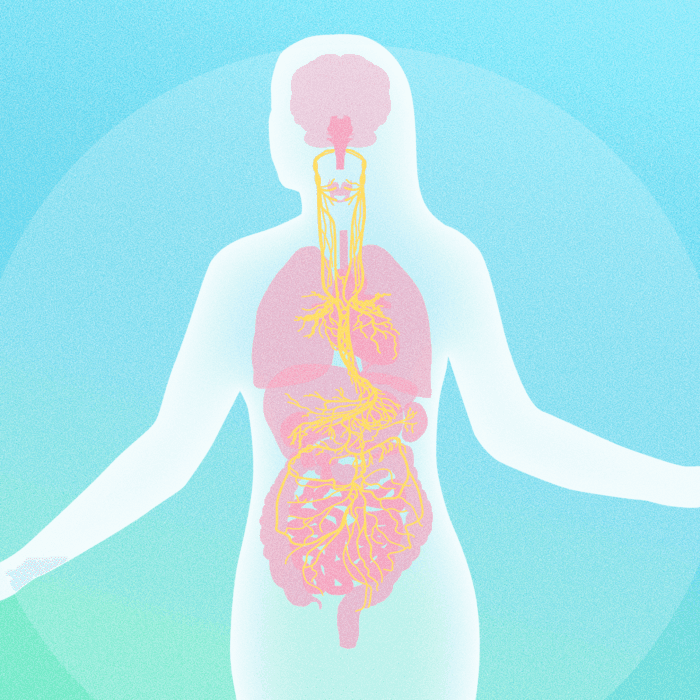
It connects to key organs such as the brain, heart, lungs, gut, and pancreas, supporting health and standing ready to address a range of challenges with both immediate and long-lasting effects.
How It Affects Your Organs
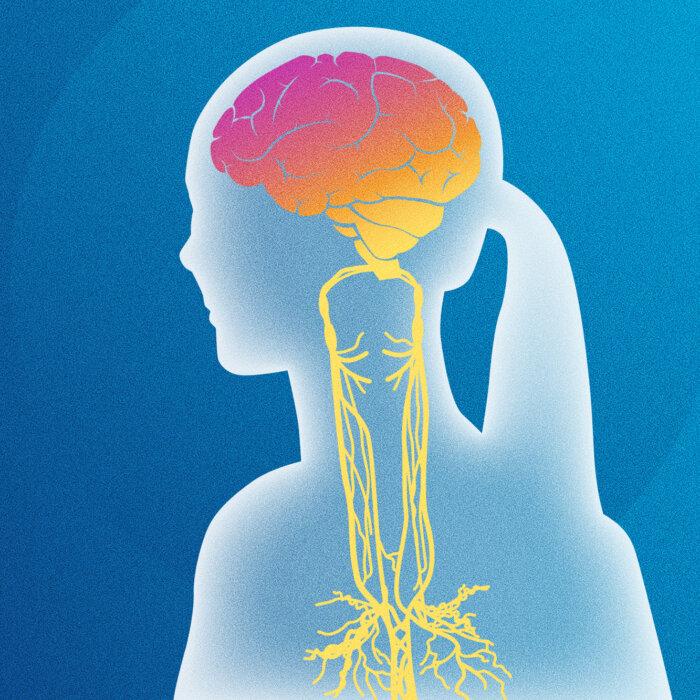
As the vagus nerve originates from the brain and travels throughout the body, it branches into various organ systems.It’s part of the parasympathetic nervous system, which means that its primary role is to calm and restore your body’s balance. When the vagus nerve stimulates these organs, the parasympathetic (rest and digest) response is activated, Dr. Priyal Modi, an integrative medicine practitioner, told The Epoch Times.

Brain
Stimulating the vagus nerve relieves symptoms of depression and anxiety and builds stress resilience.Heart and Lungs
The vagus nerve keeps both heart rate and breathing steady to ensure that all tissues get a steady supply of oxygen.Gut and Pancreas
The vagus nerve coordinates energy use, digestion, and appetite.It mobilizes food through the digestive tract and breaks it down. It is also connected to the brain regions that influence hunger and satiety, helping you know when you are hungry or full.
Immune System
Stimulating the vagus nerve helps reduce inflammation and maintain a healthy immune system.Monitoring Vagal Health
Vagal tone—or the influence that the vagus nerve has on the body—is a reflection of the health of the vagus nerve itself, according to Modi.A Look Ahead
The state of the vagus nerve is linked to various conditions, ranging from mental health disorders to Alzheimer’s disease.There are many approaches to improve vagus nerve function, such as vagus nerve stimulation—often defined as mechanical stimulation using a vagus nerve stimulator—and natural stimulation methods.
Breathing, for example, is a distinct natural stimulator because it’s the only part of the autonomic nervous system that operates both automatically and consciously, giving us direct access to influence the vagus nerve system.
People respond to different types of therapies in unique ways; treatments, in general, must be tailored to a person’s needs and what’s accessible to them. However, stimulating the vagus nerve is something that everyone can try, according to Lidalize Grobler, an educational psychologist.
“It’s something I rely on most in my own practice because, in our modern lives, many of us are constantly in a fight-or-flight state. Stimulating the vagus nerve can help regulate this response, making it valuable for nearly everyone,” she said.
Upcoming articles in this series will explore ways to improve vagus nerve function to alleviate a number of conditions.